Machinery Engineering Field
- HOME
- Business Information
- R&D Department
- Machinery Engineering Field
- Sintering technology of resin
- Technology of plasma deodorization
- Dry process classification to
three products simultaneously
Sintering technology of resin
Pursuing the unlimited potential of resin-sintered porous materials.

This is technology a used to mold and manufacture porous materials by sintering resin particles in a three dimensional state.
Outline of technique
Sinter-Lamellar-Filter™ (SLF) dust collector uses a resin-sintered porous material as a filter. It has a high collection efficiency that was previously difficult to achieve. Moreover, since it is a resin-sintered material, it has excellent chemical resistance and a long life.
Based on this air purification technology, we are currently pursuing the unlimited potential of sintered porous materials for various plastics.
Features
There is no what rusts because it makes the resin a raw material.
Moreover, it is also possible to add functions such as "Chemical resistance" and "Heatproof" by selecting the resin.
Structure

It is the one that the resin was sintered to three dimension structure.
Many have a gap internally by three-dimension structure like the sponge. By controlling this gap, it can be used for filtration, etc.
| Applications | collection dust, collection Product |
|---|
Technology of plasma deodorization
It is an environmentally friendly technology that eliminates gas components and odors.
By exposing the air to be processed to the plasma region, the removal effect is demonstrated.
Outline of technique
While particulate matter and smoke can generally be removed with conventional filters, gas components and odors cannot be eliminated in the same way. Our technology uses low-temperature plasma generated by our proprietary electrodes to remove these gaseous components and odors.


Features
Offensive odor air is exposed to the low-temperature plasma generated, and is oxidized and decomposed by the radical action generated by the plasma to make it harmless. In addition, through a series of processes, the gaseous components are liquefied and changed into a state that facilitates physical adsorption.
Structure and Theory
Deodorization of cigarette smoke
By combining plasma with filters and catalysts, particulate matter, gas components, and odors contained in cigarette smoke are removed. This technology can be applied to facilities where odors are a concern (such as smoking areas).
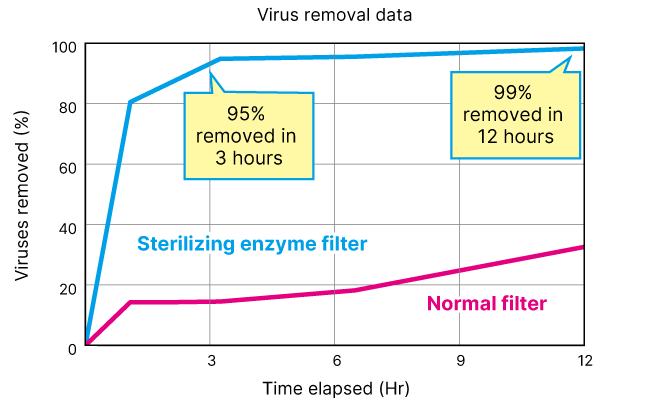
Removal of virus
By combining the plasma with an sterilizing enzyme filter and catalyst, it removes not only gas components and odors from indoor air, but also viruses, mold and pollen. It is expected to be applied to indoor air purification in hospitals and public facilities.
| Applications |
|
|---|
Dry process classification to three products simultaneously
Easy control of particle size distribution.

Elbow-jet is the precise air classifier for dry process, which is different from conventional classifier.
It can classify small particles to three products simultaneously, by using the original principle of Coanda Effect.
Outline of technique
Elbow-Jet works on the principle that the trajectory of a particle in a current of air is a function of the inertia and air resistance of that particle size.
Features
Elbow-Jet can do triple classification with simultaneous fine and coarse cuts, and can achieve sharp particle size distribution. Also, its simple structure enables easy countermeasure to abrasive.
Specifications of Elbow-Jet Air Classifier
| Model | Feed Capacity [ kg/h ] |
Total Air Flow [ m3/min ] |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| EJ-LABO | 1 - 5 | 2.0 | Automatic control (By setting up cut point) |
| EJ-PURO | 3 - 15 | 2.7 | Automatic control (For small production use) |
| EJ-05 | 10 - 70 | 4 - 6 | ↓ For production use |
| EJ-15 | 30 - 200 | 9 - 15 | |
| EJ-30 | 60 - 400 | 14 - 24 | |
| EJ-45 | 90 - 600 | 20 - 33 | |
| EJ-60 | 120 - 800 | 25 - 42 | |
| EJ-75 | 150 - 1000 | 31 - 51 | |
| EJ-90 | 180 - 1200 | 32 - 54 | |
| EJ-105 | 210 - 1400 | 41 - 69 | |
| EJ-150 | 300 - 2000 | 58 - 96 |
Structure and Theory
This classifier is very simple structure. Only putting Coanda block, two classification edges, and G block between two stainless boards.
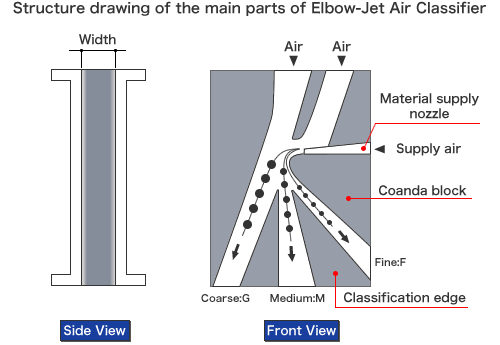
Particles are accelerated by an ejector unit and injected into the classifier by compressed air through a feed nozzle. Its jet stream tend to flow along the curved surface of Coanda block, because of "Coanda Effect"(If there is a one side wall in a passage of jet stream, the stream flow among the wall).
Each particle injected into the classifier has a different inertia dependant on its particle size (specific gravity). The smaller particles will flow near the curved surface of Coanda block with jet stream, because of its little inertia.
On the other hand, the larger particles will fly farther from Coanda Block, aparting from jet stream, because of its big inertia. By setting two movable classification edges whose position can be set easily at outlet of streams, desired classified product can be got simultaneously.
Example of classification
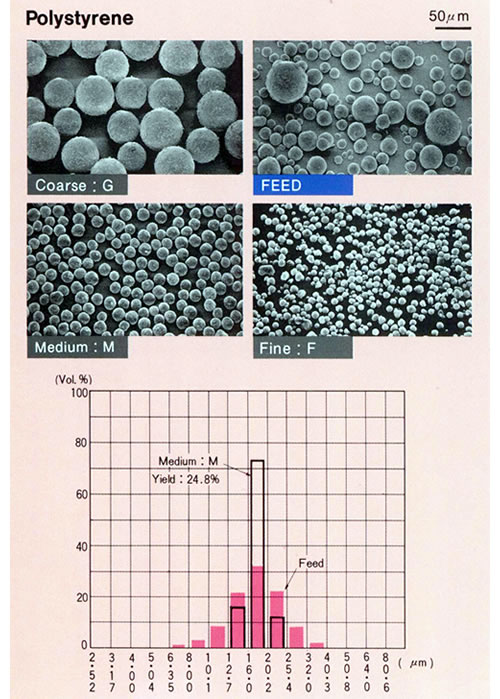
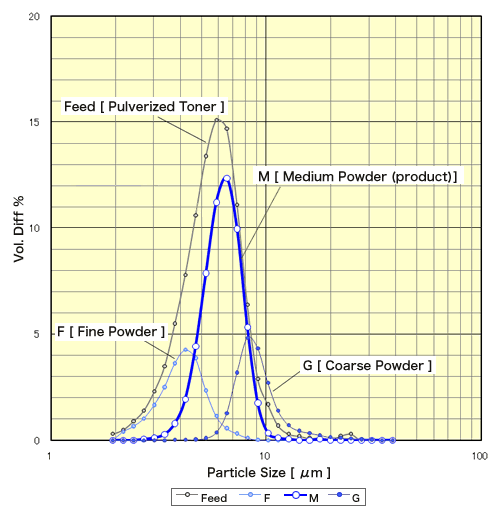
Pulverized Color Toner (polyester Cyan)
| d50(Vol.) | -4µm(Pop.%) | +12µm(Vol.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feed material before classification | 6.36µm | 41.1% | 1.9% |
| Medium of Product | 6.28µm | 11.1% | 0.2% |
| Applications | Toner (Pulverized Toner, Polymerized Toner, and Color Toner), Plastics, Plastic Beads (PMMA), Electric materials, Battery materials (Solder, Mn-Oxide, Ni, Li-Ni-Oxide), Abrasive materials (Cerium oxide, Al2O3, SiC) |
|---|

